|
|
 List navigation
List navigation
|
| Home page | TAH partonomy |
| Top level |
sensory organs  Short Extended Short Extended
|
| Level 2 |
vestibulocochlear organ (pair)  Short Extended Short Extended
|
| Level 3 |
middle ear (pair)  Short Extended Short Extended
|
| Current level |
walls of middle ear (pair) 
|
| Subsidiary language with Latin |
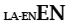 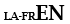 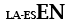
|
| Non Latin primary language |
 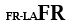 
|
 Partonomy list
Partonomy list
|
 Scientific notes
Scientific notes
|
| UID |
Libelle of note
|
| 7172 |
The promontorium gives rise to several bony ridges: (a) the ponticulus promontorii; (b) the subiculum promontorii; and (c) the finiculus.
|
| 7175 |
In the retrotympanum, lateral and medial spaces relative to the facial nerve and pyramidal eminences were defined: lateral, the sinus facialis and the sinus tympanicus lateralis; medial, the sinus tympanicus posterior and the sinus tympanicus.
|
| 7181 |
The paries mastoideus shows three bony eminences, each giving rise to a ridge: (a) the eminentia pyramidalis; (b) the eminentia chordae tympani; and (c) the eminentia styloidea.
|
| 7187 |
See note # 7175
|
| 8190 |
For the paries auris mediae, several new terms have been added giving credit to clinical findings (from Mansour S. Magnan J, Ahmad Hh, Nicolas K, Louryan S 2019 Comprehensive and Clinical Anatomy of the Middle Ear, 2nd ed. Springer, Cham).
|
| 8205 |
New term; the Ponticulus promontorii is a thin bony bridge from the Eminentia pyramidalis to the Promontorium (from Lang J 1992 Klinische Anatomie des Ohres. Springer, Wien - New York).
|
| 8208 |
The chorda tympani passes from the facial canal through the posterior tympanic canaliculus to enter the tympanic cavity via the apertura tympanica canaliculi chordae tympani posterioris; via the apertura tympanica canaliculi chordae tympani anterioris, the chorda tympani enters the anterior tympanic canaliculus (see also TA98, A02.1.06.011 canaliculus chordae tympani)
|
| 8380 |
See note # 8208
|
| 14061 |
The promontorium shows a bony overhang over the cochlear or round window, comprising a postis anterior (anterior pillar), a roof (tegmen) and a postis posterior (posterior pillar) as described by Bolobas B (1972 A hallószery mikrochirurgial anatomija. Könykiadó, Budapest (in Hungarian); Proctor B, Bolobas B, Niparko JK 1986 Anatomy of the round window niche. Acta Otol Rhinol Laryngol 95:444-446). For the tegmen, the term canonus fossulae fenestrae cochleae has been suggested as it forms a canopy overhanging the cochlear window (Topsakal V, Matulic M, Assadi MZ, Mertens G, Van Rompaey V, Van de Heyning P 2020 Comparison of the surgical techniques and robotic techniques for cochlear implantation in terms of the trajectories toward the inner ear. J Int Adv Otol 16:3-7).
|
| 14062 |
See note # 14061
|
| 14063 |
See note # 14061
|
| 14064 |
See note # 14061
|
| 14065 |
See note # 14061
|
| 14078 |
See note # 7175
|
| 14079 |
See note # 7175
|
 Signature
Signature
|
| Type of list | P4 |
| List Unit Identifier | 8190 |
| Number of children | 166 (validated) |
| Number of units | 60 (validated) |
| Signature | 23227 (validated since 30.7.2024) |
| Date: 25.06.2025 |



